Penile implants, or prostheses, are highly effective means of restoring erectile function for men who do not respond to simpler measures. In many ways, penile prostheses are as quality-of-life-restoring as are total joint replacements to those suffering with arthritis, converting penile “cripples” into functional males with restored erections and resolution of the psychological and emotional anguish resulting from the loss of virility and vitality.
Since the penile prosthesis first became available over forty years ago, numerous refinements, modifications and innovations have been made. The current iterations are sophisticated and well-engineered devices composed of medical-grade synthetic materials. They are surgically implanted under anesthesia, typically on an outpatient basis. They are totally internal, with no visible external parts and function to provide sufficient penile rigidity to permit penetration. For the right man under the appropriate circumstances, the penile prosthesis can be a life changer.
Penile sensitivity, sex drive and ability to ejaculate are essentially unchanged following implantation of a penile prosthesis. Unlike a normal erection, a penile prosthesis does not result in swelling of the head of the penis nor the erectile tissue surrounding the urethra. Nonetheless, it results in a penetrable and durable erection that can restore sexual function in a man who is incapable of achieving an erection.
Types of penile implants
There are two types: semi-rigid and inflatable. The difference between these two implants is the distinction between a Volkswagen and Mercedes, both effective and functional, but the latter with many more “bells and whistles.” In either case, the dimensions of one’s erectile chambers are precisely measured in order to size the implant properly, similar to measuring the length and width of your feet in order to ensure a good shoe fit.
Both semi-rigid and inflatable varieties of prostheses can be highly beneficial in men with ED following treatment for prostate cancer who have not responded to simpler measures.
Semi-rigid penile prosthesis
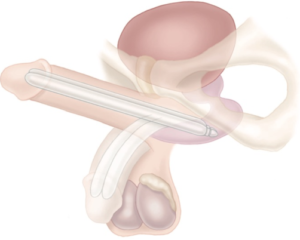 A semi-rigid penile prosthesis (a.k.a. malleable implant) is a “static” implant that always remains rigid, not unlike the penile bone present in many primates, except that it can be hinged. It is bent upwards for sexual use and downwards for concealment. It consists of two malleable cylinders that are implanted within the paired penile erectile chambers through a small incision. Its advantage is its simplicity, the fact that it is less expensive than an inflatable device and its utility for patients with dexterity issues and for those with a limited reach. Its disadvantage is that it cannot go from an inflated state to a deflated state as can the inflatable penile implant, thus creating potential concealment issues. Furthermore, by virtue of the constant pressure of the implant on the soft tissues of the penis, it can be more uncomfortable than the inflatable variety and has the potential for thinning the penile flesh.
A semi-rigid penile prosthesis (a.k.a. malleable implant) is a “static” implant that always remains rigid, not unlike the penile bone present in many primates, except that it can be hinged. It is bent upwards for sexual use and downwards for concealment. It consists of two malleable cylinders that are implanted within the paired penile erectile chambers through a small incision. Its advantage is its simplicity, the fact that it is less expensive than an inflatable device and its utility for patients with dexterity issues and for those with a limited reach. Its disadvantage is that it cannot go from an inflated state to a deflated state as can the inflatable penile implant, thus creating potential concealment issues. Furthermore, by virtue of the constant pressure of the implant on the soft tissues of the penis, it can be more uncomfortable than the inflatable variety and has the potential for thinning the penile flesh.
Inflatable penile prosthesis
The inflatable penile prosthesis is a “dynamic” hydraulic implant designed to mimic the characteristics of a normal erection. It can be inflated and deflated at will by virtue of a self-contained hydraulic system. Cylinders (inner tubes) are implanted within the paired erectile chambers. The control pump is implanted in an accessible area of the scrotum. The third element is the reservoir that contains the fluid necessary for inflation, which is typically implanted behind the pubic bone or the abdominal wall. Tubing connects the control pump to the cylinders and to the reservoir.
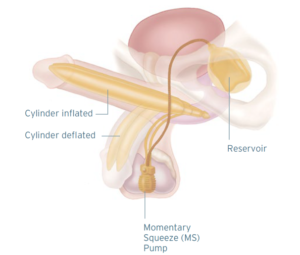 When an erection is desired, the scrotal control pump is repeatedly squeezed, which transfers saline from the reservoir into the penile cylinders. As the cylinders fill, an erection develops and with each consecutive squeeze, more fluid fills the cylinders, creating a more rigid erection of wider girth. The erection will remain until the release bar located at the upper aspect of the control pump is activated. After the completion of sexual intercourse, by pressing this release bar, the fluid in the cylinders returns to the reservoir where it is again stored, returning the penis to its flaccid state. Some inflatable implants are designed to increase in girth only, whereas others increase in length and girth.
When an erection is desired, the scrotal control pump is repeatedly squeezed, which transfers saline from the reservoir into the penile cylinders. As the cylinders fill, an erection develops and with each consecutive squeeze, more fluid fills the cylinders, creating a more rigid erection of wider girth. The erection will remain until the release bar located at the upper aspect of the control pump is activated. After the completion of sexual intercourse, by pressing this release bar, the fluid in the cylinders returns to the reservoir where it is again stored, returning the penis to its flaccid state. Some inflatable implants are designed to increase in girth only, whereas others increase in length and girth.
Advantages of the inflatable implant are its ability to inflate and deflate, mimicking normal erectile function and creating no issues with concealment. The penis can be kept rigid for as long as desired and will not deflate after ejaculation, unlike the flaccidity that occurs after ejaculation under normal circumstances. Disadvantages include its additional expense, — although it is usually covered by insurance — the fact that it requires some degree of manual dexterity to operate, and the fact that it is more susceptible to mechanical malfunction than the semi-rigid variety because of its complexity.

